On-Axis Guider
We have some ways to track stars' motion accuratelly. Popular ways are probably to use a guiding scope and to use a off-axis guider. Recently, CCD camera have a second chip for guiding, but we have no most simple way, on-axis guider. On-axis guider should give the axis ray onto a guiding chip by a beam splitter( BS ). However, the thickness of this BS causes astigmatism because of its tilt, so the on-axis has been never developed yet. See the second image, you see the oblate stars nea
r the focus point by single BS.
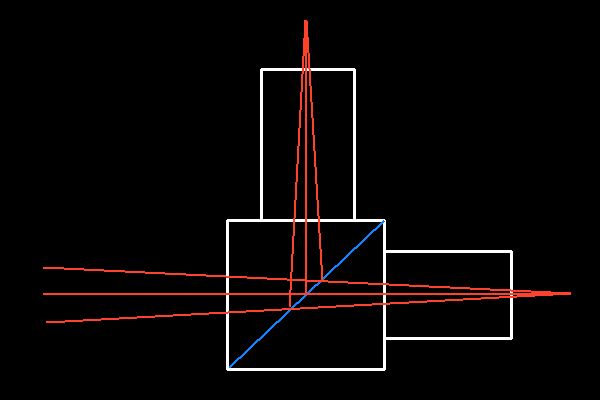 Basic ray diagram of on-axis guider
Basic ray diagram of on-axis guider
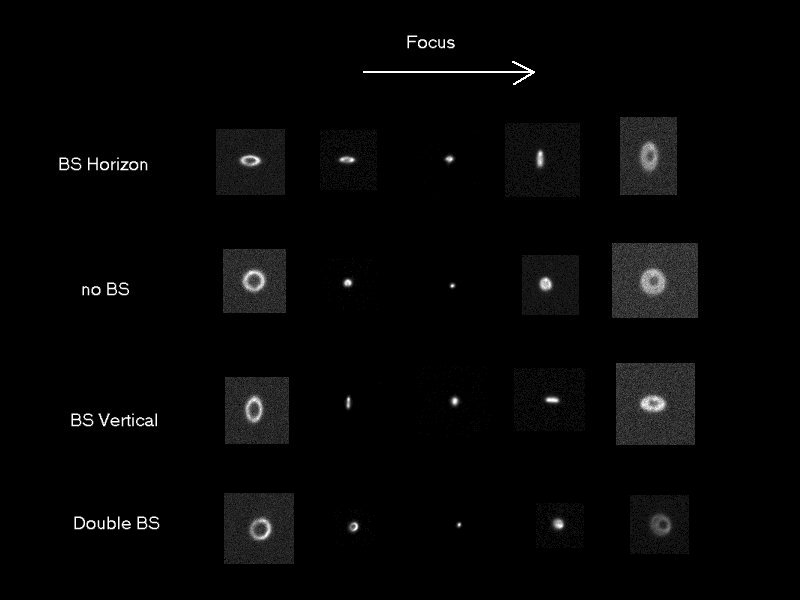 Defocus image of a star.
Defocus image of a star.
To cancel this astigmatism, another tilt BS, so-called astigmatism-correcting plate( maybe as-correcting plate), is needed. I made a prototype on-axis guider and tested taking images. One of them is at bottom defocusing image in the upper image. It was succesful, and I convinced that the on-axis guider was most convinient for tracking stars.
 Ray diagram of on-axis guider.
Ray diagram of on-axis guider.
In the 1st prototype on-axis guider, I used two no-coated glass plates as BS and as-correcting plate, and those two filters were not set 45 degree perfectly, so the defocus images were still oblate slightly. The reflection of the glass surface is 4% approximately, but this 4% is bright enough to detect 8th magnitude stars with 8-inch SCT. FWHM 5nm narrow band makes white light through 1.2% only, but no-coat glass plate gives 4% light to a guiding CCD.
Next image is the first light with the 2nd prototype on-axis guider which uses a hot mirror instead of no-coated galss plate, and a multi-coated plate is used as as-correcting plate. The hot mirror reflects more than the no-coated glass plate, so it was easy to find a guiding star. Furthermore, an imager shifter was set on the guider, and the chance to find a star is much higer.
 Horse Head nebula ( IC434 / B33 )
Horse Head nebula ( IC434 / B33 )
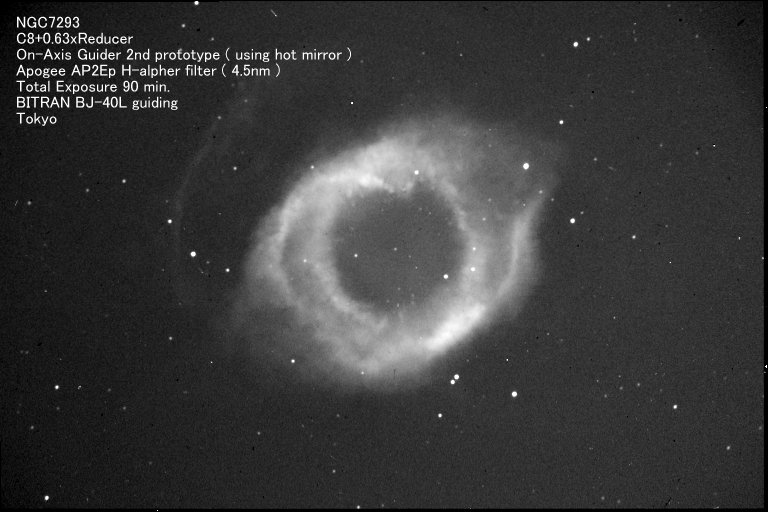 Helix nebula ( NGC7293 )
Helix nebula ( NGC7293 )
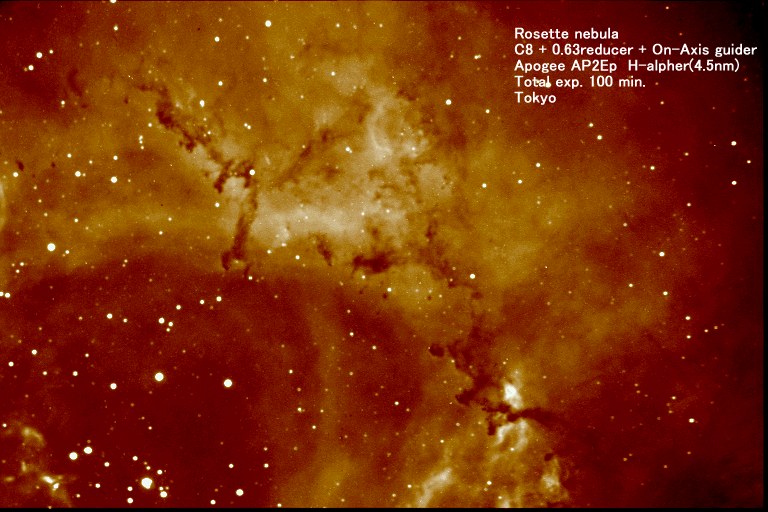 Rosette nebula
Rosette nebula
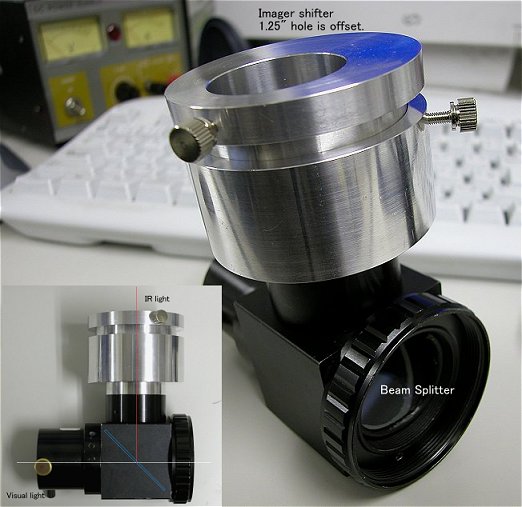 Watch the offset 1.25" hole. Rotating this 1.25" adapter gives wider area.
As-correcting plate is set in the imaging camera.
Watch the offset 1.25" hole. Rotating this 1.25" adapter gives wider area.
As-correcting plate is set in the imaging camera.
Those prototype reflects IR ray onto a guiding CCD and trasfers visual ray to an imaging CCD this case. There are another way, which reflects visible ray to an imaging CCD. The merit of this way is no astigmatism in the reflected ray. However, no good hot mirrors are saled now, so I am asking to a company to make a perfect hot mirror.
Mail to me about CCD Format
October 16th, 2003







